Tree algorithms
- Tree center(s) - O(V+E) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - > Here !
- Tree diameter - O(V+E)
- Rooting an undirected tree - O(V+E)
- Lowest Common Ancestor (LCA, Euler tour) - O(1) queries, O(nlogn) preprocessing
Tree Center(s) 개요
Graph 에서 Center를 찾는 알고리즘이다. 다만, 제한조건이 존재하는데 그래프는 Undirected 하고 asyclic 해야한다.
그래프에서는 Undirected & asyclic 조건을 만족하면 'Tree'라 정의하기 때문에 Tree Center(s)라 불린다.
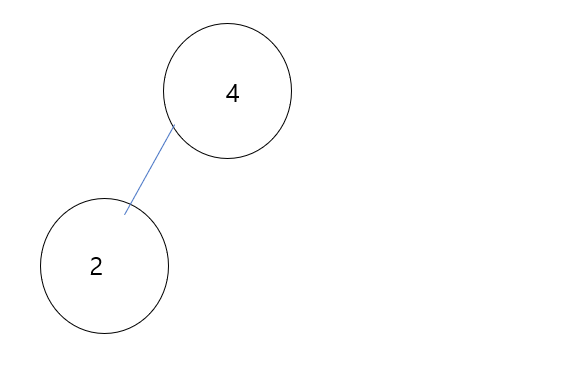
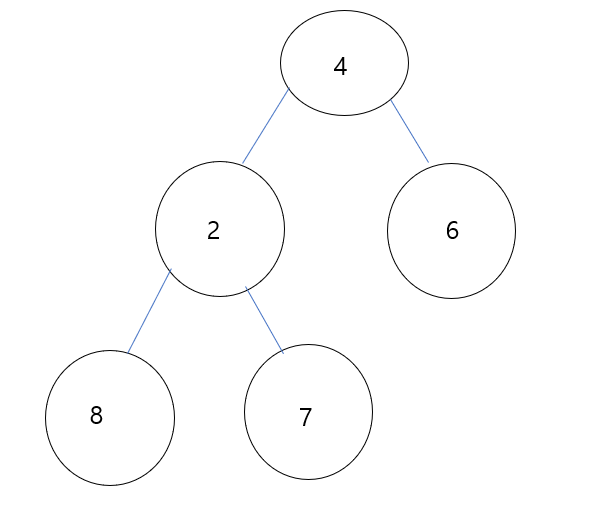
아래 예시를 보자.


=> Graph에서 가장 긴 Path의 중점이 Center(s) 이다.
How to Solve ?
Tree의 Center를 찾기 위한 방법이 상당히 재밌는데,
Leaf 노드들을 bfs로 쳐냄으로써 Center(s)를 찾아낸다.
다시말해, degree가 1인 leaf들을 bfs로 쳐냈을 때, 마지막에 잔재했던 leaf node(s)가 Center가 된다.
### pseudo code
def findTreeCenters(n: int, graph: dict[List[]]) -> List:
"""
@param n : the size of vertexes.
@param graph : adjacency list.
graph는 asyclic, undirected 해야함.
e.g.
graph[1] = [0,2,3]
0 --- 1 --- 2
|
|
3
"""
degree = [0] * n
for i in range(n):
degree[i] = len(graph[i])
## 쳐내고자 하는 leaf들을 찾는다.
leaves = []
for node in range(n):
if degree[node] == 1:
leaves.append(node)
## center를 찾기 위한 반복문.
## 지속해서 leaf를 쳐낸다.
count = len(leaves)
while count < n:
new_leaves = []
for leave in leaves:
## leave를 쳐냈으므로 degree는 0이 돼야함.
degree[leave] = 0
for neighbor in graph[leave]:
degree[neighbor] -= 1
if degree[neighbor] == 1:
new_leaves.append(neighbor)
leaves = new_leaves
count += len(leaves)
return leaves
어디에 사용될까 ?
Identifying Critical Nodes: The center(s) of a tree often represent the most critical or central nodes in the network, which may play crucial roles in maintaining the connectivity of the graph.
Rooting Trees: In computer science and data structures, you might need to root a tree at a specific node. The center of the tree can be used as a good root that balances the tree.
Network Design: Finding the center(s) of a network can help in designing efficient communication networks or transportation systems.
Tree Center는 특히 네트워크에 유용하게 사용될 수 있을 듯 하다.
추천 문제
https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-height-trees/
Minimum Height Trees - LeetCode
Can you solve this real interview question? Minimum Height Trees - A tree is an undirected graph in which any two vertices are connected by exactly one path. In other words, any connected graph without simple cycles is a tree. Given a tree of n nodes la
leetcode.com